Google Penalty Primer : A First Timer's Guide To Hell

updated November 2023
Q: How Do You Know You're Penalized?
Google considers your site penalized if you have a manual action penalty flagged in Search Console.
But that only covers recognized penalties:
- pure spam,
- unnatural links to your site,
- cloaking and/or sneaky redirects,
- thin content with little or no added value,
- hidden text and/or keyword stuffing,
- spammy free hosts,
- user generated spam,
- possibly others unnamed.
But even if you're is not doing any of that forbidden stuff, your rank loss can still be the equivalent of a Google penalty. It's just hidden under the ever-changing, secret algorithm, and you're being penalized for something you're on your own to discover.
The nature of rank losses we're seeing has shifted significantly over the past 10 years, and the solutions less obvious. The landscape has become more technically sophisticated and the sources of problems has grown and diversified. For example, your rank problem might now be due to your cms. We've found problems linked to themes purchased for Wordpress and Shopify causing failures in Core Web Vitals tests and the accountability has shifted away from the platform towards the theme.
When trying to solve a rank loss mystery, start with the obvious risks. Review recent development work. Some of the most common self inflicted wounds come from developer errors. Changing a url without redirecting it, assigning the wrong canonical, deleting a script, redirecting to a non-existing url, etc.
Make sure your domain and any url involved in the rank loss are still indexed & cached. Request indexing of any dropped url.
Run an audit to discover addressable technical issues that could prevent indexing. Every site has technical issues, but minor issues are unlikely to trigger a collapse. But don't ignore duplicate or multiple versions of title and description meta tags.
Parent/Child
Lately Google has seemed easily confused by certain kinds of markup used in tags, filenames and on page semantics. This is labelled parent/child because it's most commonly seen when category (parent) searches show a rank held by a product (child) url. But the problem is bigger than this simple explanation. Often the url that should be holding the rank will be swapped out for a url that may or may not be related. We've seen many examples of this in the past 5 years - so much so that we've instituted strict nomenclature rules for the most important tags that contribute to rank signals.
For example, if the category is "Batman t shirts", that is usually the title tag. But if products have title tags like this: "Batman T Shirts The Dark Knight" where the category is followed by the style, this may create confusion for the Googlebot. We can avoid this by reordering the title tag to "The Dark Knight Batman T Shirts". This works because the order of the words in the title tag is very important - first words are most important. This is also why we don't use qualifiers first - never "Best Batman..."
When a url goes off line, it usually takes a while before it stops showing up in the serps.
Index check
updated 16 January 2015
Q: All penalties have a timeline from 48 hours to months. What’s the maximum?
“They can go pretty far. For total horribleness, the penalty can stay until the domain expires.” (Matt Cutts, June 2013 SMX)
There's really nothing quite like the experience of typing in your main keyword only to find your site no longer at the top of the results. The resulting panic has no doubt triggered heart failure for some poor site owners, although we'll never see those stats. But the numbers of sites getting tanked by penalties is not small. So if you just discovered you're penalized, take comfort in the fact that you're not alone.
Manual Actions - Human Imposed Penalties
Google takes "manual actions' against websites that they perceive to be harmful to the search, or to Google. Because of the huge consequences of such actions, Google did not even acknowledge penalties until only very recently, and even then on a very limited basis. It is very likely that if you are penalized, you won't hear about it from Google. This is changing, ever so slowly, and if you received a message in Webmaster Tools that you are in violation of the guidelines, consider yourself very lucky. The vast majority of penalties come unannounced and therefore with no direction for cure. A message from Google may even be specific - we're aware of messages referencing paid links and doorway pages.
Over-Optimization Penalty For Unnatural Links
Here's an actual message from Google that you never want to see. This one telling you that you have "unnatural" links:
We've detected that some of your site's pages may be using techniques that are outside Google's Webmaster Guidelines.
Specifically, look for possibly artificial or unnatural links pointing to your site that could be intended to manipulate PageRank. Examples of unnatural linking could include buying links to pass PageRank or participating in link schemes.
We encourage you to make changes to your site so that it meets our quality guidelines. Once you've made these changes, please submit your site for reconsideration in Google's search results.
If you find unnatural links to your site that you are unable to control or remove, please provide the details in your reconsideration request.
If you have any questions about how to resolve this issue, please see our Webmaster Help Forum for support.
Sincerely, Google Search Quality Team
However unwelcome this message, it's way better than just getting penalized without notice. At least in this instance you kind of know why.
2 Different Ways To Be Penalized For Unnatural Links - Penguin And Manual Actions
Penguin is an automated update that harms sites for unnatural links without triggering a manual action notice in WMT. So if you're hit with this one, you not only have to disavow the links, but you also have to wait until the next update to see the benefit of those disavowals. Penguin launched on 24 April 2012. This was a serious penalty - if you were penalized and corrected the problem after 4 October 2013 (Penguin update), you would not see improvement until the 17 October 2014 update! And because there is no manual action, you have no access to the form to file for reconsideration. The process is entirely automated, which means that you can rely on the disavow tool rather than link removals.
 So if you have to be penalized for your links, you might prefer a manual action. This permits you to quickly remove the links and request reconsideration. But this comes with a requirement that some effort to remove the links be made.
So if you have to be penalized for your links, you might prefer a manual action. This permits you to quickly remove the links and request reconsideration. But this comes with a requirement that some effort to remove the links be made.
Penalties for unnatural links have been around for a long time, and in the most common cases (you hired someone to build links) the fix is simple in principle: vet the links, then remove and/or disavow the problem links. The issues lie not only with identifying the links, but also with the actual removal process - especially very large numbers. And there is risk of further damage - even with smaller numbers, you need the ability to distinguish between the good and the bad. If you remove or disavow without thoroughly vetting those links, you can easily end up removing links that were supporting your ranks.
Panda
Starting in February 2011, Panda has been attempting to identify and suppress low quality content, meaning thin, copied, automated, jibberish, over-optimized, etc. Sites could avoid the early Panda updates just by keeping their content original, deep and by providing genuinely useful information. If you were automating geo targets into content across many urls, using templates to create content, pulling your content from other sites, or distributing your content to be used by others, Panda ate your lunch.
Whether the problem is over-optimized content or links, domain level issues, etc., the key to recovering from previous Google penalties was in addressing something called "search compliance" - being non-compliant gets you penalized. Compliance covers everything from the server implementation, status of other owned sites, content, markup, links, etc. with rules that we all understand once exposed to them. So no keyword stuffing, no hidden text, no spammy links or content, etc.
Updates Starting With Panda 4+ Are Enforcing Standards On Content Presentation
The May 2014 updates to Panda introduced a huge change in the way sites are evaluated. The resulting reordering has harmed many sites that are genuinely relevant - in some cases THE most relevant, but do not meet the new standards. These sites are recovering, often not by changing their content, but by altering the presentation in ways that improve user experience. We see improvement when sites that used to display only plain text add images, content specific links - either embedded or in a separate nav container - h1, h2, etc. subtitle cascades, links to outside authority content, co-citation of related important terms, inclusion of video & other media, etc. In many respects, this is forcing sites into better layouts and strategies that engage the reader and motivate opportunities to click.
Finding The Cause
In order to recover, you have to know why you lost your ranks, and the extent of the problem. Look at your search traffic in Google Analytics and see if sharp drops line up with the dates of Penguin and Panda updates - you can do this using tools like panguin tool to graphically view traffic and updates on the same chart. This is not a foolproof technique, as the exact dates of updates may not correspond to the date that your site is impacted. But if you see a peak coinciding with an update, followed by a sharp decline, learn about what that update was targeting.
Panguin Tool:
Fruition Penalty Checker:
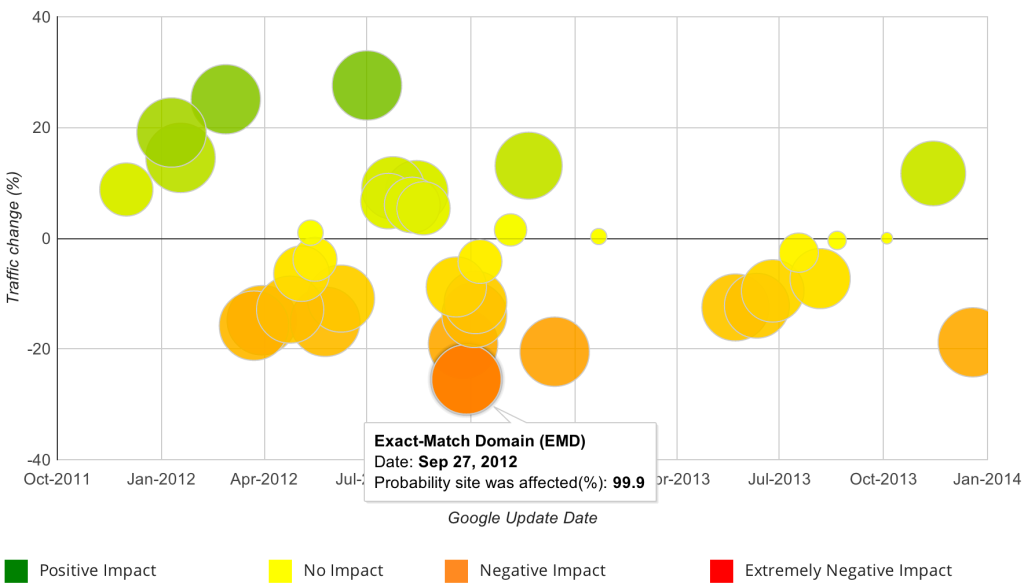
Beyond the lining up of traffic moves with update dates, any additional metric (like probabilities) are dependent on information that may not be measurable. This hold true for all tools that offer evaluation, especially tools that evaluate the quality or risk of links. Take automated link evaluation advice at your own risk. Even the most popular tools fail our standards, and the cheapest solutions are always the most flawed. So always seek confirmation if possible.
Negative SEO
It is possible for a third party to use Google's enforcement actions against competitors by triggering penalties, usually involving link schemes. Since Google cannot know the source of the intent of links to your site, we have experienced many instances where a site was victimized. In these instances many consider Google to be complicit in the damage done to the business, due to poor policies in place to manage the damage done by these attacks. And because Google's Webmaster Tools only permits reconsideration requests to be made when a manual action is involved, if you catch an attack before you are penalized, you have no way to communicate this to Google. Small sites in competitive markets that hold high ranks are especially vulnerable. Attacks can be managed using the disavow tool once the attacking urls are known. But if an attack is successful in triggering a rank loss, your biggest challenge will be convincing Google.

Value & Limitations Of Webmaster Tools For Penalty Remediation
In addition to the above problem regarding the inability to contact Google unless you have incurred a manual action penalty, there are some other limitations regarding functionality and availability of data. For example, you are only able to download a sample of the links Google is holding you to account for. Often that sample is tiny compared to the actual number of links they display. When removing links and filing reconsideration requests, Google will often offer help by giving you examples of problematic links that have been overlooked. We have had many instances where, after downloading the WMT link data, those example links were not present in the download. If the link cleanup/reconsideration process is not succeeding we encourage webmasters to expand the link data to sources like ahrefs.com and majesticseo.com.
Another issue with WMT is that in order to properly manage your site, you need to have every possible version present in the account. For example, every subdomain needs a separate listing and undergo a separate verification process. So the www version is separate from the non-www version. Same for https versions. If you have both http and https urls, you may need 4 listings
- https://www.domain.com
- https://domain.com
- http://www.domain.com
- http://domain.com
If you include subdomains, you can easily see how the number of listings in WMT could rapidly become cumbersome.
Rank Loss Due To Indexing Issues
If a url for some reason is not indexed, even when included in a sitemap, Google provides a special "Fetch As Google" tool that permits a site owner to submit urls in order to force indexing. But sometimes this tool fails to correct indexing issues.
Fetch As Google
When it's working properly, the "Fetch As Google" tool is invaluable in remediation efforts. It's a powerful capability enabling the rapid repair/replacement of valuable pages. Submitting an unindexed file can get it indexed instantly. With a weekly limit of 500 fetches, you can see how this might be valuable during recovery. There's also a more powerful, but limited option (10 per month) where you can request both the indexing of a file and the following of all links on the page. Be warned that sending conflicting requests in close order may get them ignored. Whenever abandoning a page is necessary, use this to immediately get a replacement url indexed.

URL Removal Tool
Another valuable tool for penalty work within WMT is the "URL Removal Tool" that can assist in the removal of conflicts within the index. If you find 2 or more indexed urls with the same content, you probably should correct this with a redirect/rewrite, canonical, noindex, or other instruction. But even if the live site is corrected, the conflict will continue in the index until the Googlebot revisits all urls involved. You can often hasten the process by manually removing urls that no longer render but may still be creating conflicts in Google's index. In order for a request to be honored, the urls in question must be blocked by robots.txt, robots meta noindex, or redirection. While url removal/deletion may seem scary, there's a failsafe built in - you can revert the removal anytime within 90 days. This gives us some comfort when running experiments that could otherwise leave permanent damage in their wakes.
Penalty Information From Google
Videos from Google:
General Information:
Reconsideration:
The reconsideration form is only accessible from Webmaster Tools if there is a manual action flagged on the site. If you experience rank loss and there is no manual action indicated, then you have no way to communicate the issue to Google. All the automated updates enforce the guidelines - that is, they suppress ranks - without flagging a manual action.
 Stay Current
Stay Current
If your business relies on high ranks, you are at the mercy of the evolution currently underway in the search. In addition to constantly upping the standards, Google is moving in the direction of more automation, so sites that don't stay current with new requirements are at a distinct disadvantage. The reasons for poor search performance may no longer include only penalties. Sites with relevant content may underperform competitors that achieve higher ratings on user experience, engagement, presentation. Basically, high ranking sites will need to achieve a higher level of sophistication, creating more compelling options for users to interact with content. So stay current. It's much more difficult to catch up after experiencing rank loss than it is to avoid it in the first place.
Stay Current
Google Penalty - wikipedia.comGoogle Penalty News - searchengineland.com
Record Of Algorithm Updates - moz.com

