Google Penalty Solutions
updated 10 January 2015
Know The Cause
Most clients know why they're penalized when they first come to us. In some cases, using tools, we are able to observe rank/traffic loss corresponding with the release of an update, which can support evidence of a specific penalty. In every case, it is important to understand what triggered the penalty, whether more than one issue may be involved, and what is the level of severity.
From Penalty To Reward
In the past, and up until Panda 4+, the solutions to Google penalties always involved the remediation of compliance breaches. Basically, sites were punished for breaking rules - penalized for something they did. So the solutions often involved stopping something that was being done intentionally to gain an advantage - think hidden text, spammy links, etc.
By contrast, as we help sites recover from the recent Panda updates, the fixes do not involve ceasing some behavior, but rather doing more to enhance the user experience. Sites recover, not by changing the content, but by improving the presentation of that content. Ranks improved dramatically with the addition of engagement elements such as images, video, other media, subtitles, page specific nav, authoritative citation, and other layout improvements. Clearly this update is doing more than looking for cheaters and spam.
In the past, sites were punished for doing something that Google did not like. Now, Panda appears to be punishing sites for expectations they are NOT meeting. But I believe a more appropriate framing of the issue is that Panda's intent is to 'reward' sites that offer both relevance and engagement, as opposed to harming sites that don't. This approach serves Google's interests because it achieves search results that are not only relevant, but also provide the best user experience. Rewarding sites that engage also enables positive buy in from the development community.
So Google penalty solutions will continue to involve compliance with all the best practice guidelines, but now they will include the integration of engagement elements as a requirement.
Understanding Penalties
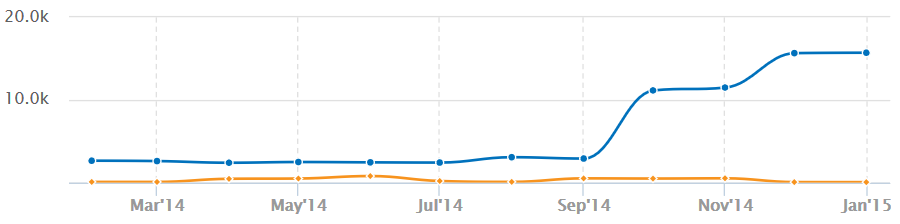
The chart below is of a site that has been penalized multiple times over several years, taking the traffic to zero.

Below is the chart of a site recovering from Penguin in October 2014.
If you're observing persistent rank loss there are techniques you can use to determine if your site is actually penalized, and draw informed conclusions as to the cause. Run a quick check to eliminate technical issues. Many people assume their site is penalized when it fails to hold significant search positions after many attempts to rank for a specific keyword. But a penalty is much more serious than simple rank failure. A penalty is PUNISHMENT for failing to abide by Google's guidelines. And although an accurate diagnosis is necessary to remediate, the exact cause can remain hidden if there is more than one issue. Also, Panda with its own quality rating system brings significant complexity to the mix.
You know you're penalized if you have one of these notices under "Search Traffic" -> "Manual Actions" in WMT:


Clients have received notices for other offenses, including outbound links and doorway pages.
If your rank loss corresponds with the receipt of a message in Webmaster Tools like the above, consider yourself penalized. And lucky. Lucky because you know the cause.
Visualizing Penguin
As an automated update, you get no notice in WMT when harmed by Penguin - AND you have to wait for the next Penguin update for the system to recognize any work you've done on link removals/disavows. This means that to diagnose a Penguin attack you need to observe the search traffic chart against the dates of the updates.
These 3 charts demonstrate a Penguin penalty that launched on 24 April 2012. The charts show various time frames on different sites. You can see that while some sites got smacked hard, others were harmed more subtly.
The first shows the link building succeeding up until Penguin strikes. The 2.0 update causes further damage starting 22 May 2013. Notice how gradual the loss was relative to the next example - took 6 months vs 5 days to reach the low.

This was a crash and burn in 5 days.

The percentage loss in the chart below is not as significant as the other two, and could very easily have gone unnoticed since this business is not totally dependent on search. Once it was discovered, this site recovered most of its traffic by submitting disavows immediately, but traffic came back one and a half months later when Penguin updated on 26 May 2012. You have to wait for Penguin updates to see the benefit of your disavows.

Solutions For Penguin & Unnatural Links Manual Actions
Since both Penguin and unnatural links manual actions are link penalties, both require an analysis of your link profile. While both penalize specific keywords and urls, there are significant differences in how these are discovered and resolved.
If your site is hit by Penguin, because this is an automated update, you will not receive a manual action notice, and you are not able to file a reconsideration request. Once you have confirmed to your satisfaction that Penguin is involved, the solution is to identify and disavow all problem links. Unfortunately you need to wait for the next Penguin update to be credited for your work.
If you received a notice in WMT like the above, you will need to not only identify the problem links, but also make an effort to remove them. In WMT, you have access to both the disavow tool and the reconsideration form. It is not recommended that you request reconsideration without making a good faith effort to remove the bad links, or to file by only disavowing them. Any links you cannot remove, you can disavow.
Visualizing Panda
As an automated update, you get no notice in WMT when harmed by Panda. There is a message for thin content, which may be Panda component, but in general we're not seeing messages associated with rank loss in most cases. This means that to diagnose a Panda attack you need to observe the search traffic chart against the dates of the updates.
The chart below is for a site that was hit on the launch of Panda on 24 February 2011.

Below chart for a new site hit by the second wave of the 16 June 2011 update.

Site below was hit by the 27 April 2012 update and again on 20 August 2012.


Solutions For Sites Harmed By Panda
The unique nature of Panda requires all sites to pay attention to the new demands for improved user experience, whether or not ranks were impacted. If you escaped the last round of updates, and your site is not providing an optimum user experience, you're vulnerable. And unlike manual actions, Panda suppression comes unannounced and without an ability to file for reconsideration. So the lesson of Panda is the absolute need to work preemptively to optimize not only the quality of your content, but to also focus more attention on the quality of the presentation. Sites are now rewarded for providing relevance via engagement. for remediating or avoiding a Panda problem.
Solutions For Sites Harmed By Third Parties
There are times when recovery requires much more than addressing the content on your site or the links to it. Negative seo is one example, where large numbers of garbage links on valuable anchors are built to your site with the intent of triggering a penalty. When this succeeds in a manual action you can attempt to convince Google you were attacked using the reconsideration form that displays along with the manual action notice. Download your links and evaluate the links with the anchors that were penalized. An attack can be very obvious - lots of porn and grey market links - or much more sophisticated. Either way, one tell tale sign will be the numbers of links, and the similarity of the posts, templates, domains, etc. Convincing Google that you were attacked is not certain or quick. If the attack triggers an automated suppression, you will not be informed, you will not have access to the reconsideration form, and therefore will have no ability to inform Google of the attack. In either case, we recommend treating the attack like a penalization - identify the links - except in this case only disavow. If it's Penguin, that's what will work, if it's a manual action, inform Google that you disavowed the attack links. Unfortunately, when your ranks are destroyed by a successful negative seo attack, the burden is on you to prove it.
Another rank issue we've encountered occurs when sites copy your content. Most of the time, Google does a good job of recognizing the content creators and is able to discount copies made by other sites. But sometimes content authority is granted to sites that copied. Use copyscape.com to see if your content is copied. If sites that copied your original content rank above you for searches involving that content, you do have recourse. File a DMCA (Digital Millennium Copyright Act) claim. You do not have to have filed a copyright registration to own the rights to your content - simply creating it does this. Filing a DMCA claim is a very simple process that is free (you do have to acknowledge a $100,000 penalty for a false claim) and because the claim is filed electronically with Google, will result in the offending urls being removed from the search. This is a solution that can recover your ranks very quickly if you act as soon as you discover the problem. You have to be logged into WMT before you can access the DMCA claim form.
Solutions For Rank Loss In General
First, go read the guidelines and make sure your site abides.
Next, make sure that your site is not generating large numbers of errors via poor implementation. Run the site:domain.com searches to understand how Google has indexed your site and discover conflicts that could be harming ranks.
Google Webmaster Tools
Read the best practices guidelines mentioned above, and open a Google account for every version of your site so you have access to their Webmaster Tools information about as much information as possible. So, for example, even if your site is configured to only display with 'www' you want information on links pointing to non-www urls since you're likely being credited (or harmed) for them. If you serve secure pages that need to be indexed, you may want 4 accounts - www, non-www, https-www, https-non-www.
From WMT you can see certain metrics that signal whether your site is performing as it should. Browse these performance metrics for aberrations that coincide with the rank loss.
Especially note 'Search Traffic' -> 'Manual Actions'. Any notice here needs to be acted upon immediately. If you find a flag here and were not notified by email, set up your WMT account to email you messages. This can prevent a problem from escaping your attention.
Also, 'Search Traffic' -> 'International Targeting' then click the 'Country' tab. Make sure this setting has not been tampered with - an incorrect setting here can destroy your ranks.
Correct duplicate title and description tags flagged at 'Search Appearance' -> 'HTML Improvements'
Cog -> 'Site Settings' : This should be configured to align with how your site displays on the web as well as within WMT:
Seeking Help
Google recommends that you use the Google forums to ask for help. While the level of expertise may vary, you might learn something valuable. Also read the previous posts and threads started by other penalized site owners. There's a lot of anecdotal information out there, and when you're mysteriously penalized you're going to be forced to educate yourself.
What happens if your remediation effort fails? There are very few veteran experts you can turn to in this field. One of them is Bob Sakayama - his original posts on the google penalty topic date back to 1999, a year or so after Google first went live. He researched the phenomenon by intentionally penalizing lots of his own sites, then observed both the penalization and recovery process. If you're stuck trying to unwind a persistent suppression, we strongly suggest you contact him - his contact info is at that link. He is also responsible for the high level search performance strategies discussed on his enterprise seo site, re1y.com, which also has a lot of information and background on google penalties from the enterprise perspective (very large and/or multi-site).
Beyond the last resort is a horrible truth. It is possible to nuke a site, especially with links, in such a way as to make the domain no longer viable in the search. These are sites with massive numbers of automated links to the homepage, where the link sources are in foreign countries, and outside the reach of US law.


